本文主要深入分析 vue.js 2.6.12 版本的源码,了解底层的实现,学习 Vue.js 处理问题的方式,包括 Vue.js 初始化开始、首次渲染的过程、响应式的依赖收集、数据响应式原理、Watcher 渲染视图等。
vue 相关准备
Vue 源码地址
vue 源码目录结构
├── scripts ------------------ 打包相关的配置文件,其中最重要的是config.js主要根据不同的入口,打包为不同的文件
├── dist --------------------- 打包之后文件所在位置
├── examples ----------------- demo示例
├── flow --------------------- Vue使用了Flow来进行静态类型检查,这里定义了声明了一些态类型
├── packages ----------------- vue还可以分别生成其它的npm包
├── src ---------------------- 主要源码所在位置
├── compiler ------------- 编译相关(vue中把模板转换成render函数)
├── codegen ---------- 根据ast生成render函数
├── directives ------- 通用生成render函数之前需要处理的指令
├── parser ----------- 模板解析
├── core ----------------- 核心代码
├── components ------- 全局的组件,这里只有keep-alive
├── global-api ------- 全局方法,也就是添加在Vue对象上的方法,比如Vue use, Vue.extend,Vue.mixi等
├── instance --------- 实例相关内容,包括实例方法,生命周期,事件等
├── observer --------- 双向数据绑定相关文件
├── util ------------- 工具方法
├── vdom ------------- 虚拟dom相关 重写了snabbdom,增加了组件机制
├── platforms ------------ 不同平台的支持
├── web -------------- web端独有文件
├── compiler ----- 编译阶段需要处理的指令和模块
├── runtime ------ 运行阶段需要处理的组件、指令和模块
├── server ------- 服务端渲染相关
├── util --------- 工具库
├── weex ------------- weex端独有文件
├── server --------------- 服务端渲染
├── sfc ------------------ vue 文件解析
├── shared --------------- 共享工具代码
├── test --------------------- 测试用例
我们可以看到,Vue 在开发的时候首先会按照功能把代码拆分到不同的文件夹,然后再拆分成小的模块,这样的代码结构清楚,可以提高其可读性和可维护性。
Flow
- Flow 是 JavaScript 的静态类型检查器(在编译前做检查,类似于 C# 和 Java )
Flow 的静态类型检查错误是通过静态类型推断实现的,文件开头通过
// @flow或者/* @flow */声明1
2
3
4
5/* @flow */
function square(n: number): number {
return n * n;
}
square("2"); // Error!vue2.x 使用 Flow 来检测,而最新版本 vue3.0 使用 TypeScript ,TypeScript 和 Flow 一样都是 JavaScript 静态类型检查器,最终都会编译成 JavaScript,所以此处只针对 Flow 做了解即可。
调试设置
打包工具 Rollup
- Vue.js 源码的打包工具使用的是 Rollup,比 Webpack 轻量
- Webpack 把所有文件当做模块,Rollup 只处理 js 文件更适合在 Vue.js 这样的库中使用
- Rollup 打包不会生成冗余的代码,webpack 会生成一些浏览器支持的模块化代码
设置 sourcemap
package.json文件中的 dev 脚本中添加参数 –sourcemap,记录源码和打包代码对应关系,方便调试1
2
3
4
5{
"scripts": {
"dev": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --sourcemap --environment TARGET:web- full-dev"
}
}-w:watch 监视源码的变化,当源码发生变化时,立即重新打包;-c:设置配置文件--sourcemap:开启代码地图,在调试时,可以直接进入 src 中查看源码--environment:设置环境变量,通过设置的环境变量,打包不同版本的 Vue
通过
npm run dev执行打包,生成完整版的vue(dist/vue.js)调试
examples 的示例中引入的 vue.min.js 改为 vue.js ,打开 Chrome 的调试工具中的 source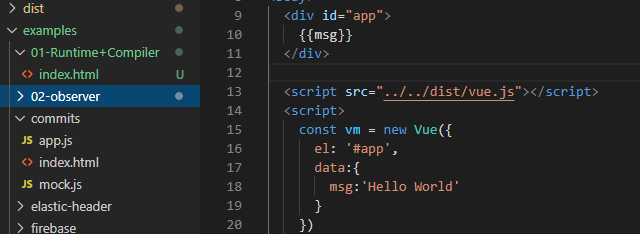
Vue 的不同构建版本
官方文档 - 对不同构建版本的解释
| UMD | CommonJS | ES Module | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full | vue.js | vue.common.js | vue.esm.js |
| Runtime-only | vue.runtime.js | vue.runtime.common.js | vue.runtime.esm.js |
| Full (production) | vue.min.js | ||
| Runtime-only (production) | vue.runtime.min.js |
- 完整版:同时包含编译器和运行时的版本。
- 编译器:用来将模板字符串(template)编译成为 JavaScript 渲染函数(render –> vnode)的代码,体积大、效率低。
- 运行时:用来创建 Vue 实例、渲染并处理虚拟 DOM 等的代码,体积小、效率高。基本上就是除去编译器的代码。
- UMD:UMD 版本通用的模块版本,支持多种模块方式,以通过
<script>标签引入, vue.js 默认文件就是运行时 + 编译器的UMD 版本。 - CommonJS(cjs):CommonJS 版本用来配合老的打包工具比如Browserify或webpack 1。
- ES Module:从 2.6 开始 Vue 会提供两个
ES Modules(ESM) 构建文件:- 为打包工具提供的 ESM:为诸如
webpack 2或Rollup提供的现代打包工具。ESM 格式被设计为可以被静态分析,所以打包工具可以利用这一点来进行“tree-shaking”并将用不到的代码排除出最终的包。 - 为浏览器提供的ESM(2.6+):用于在现代浏览器中通过
<script type="module">直接导入
- 为打包工具提供的 ESM:为诸如
Runtime + Compiler(完整版) vs. Runtime-only(运行时)
1 | // Runtime + Compiler |
项目中推荐使用运行时版本,因为运行时版本相比完整版体积要小大约 30%,基于 Vue-CLI 创建的项目默认使用基于 ESM 的方式的运行时 vue 版本,即 vue.runtime.esm.js
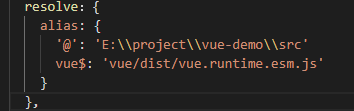
使用 Vue-CLI 创建的项目并不能直接看到 vue 的构建版本,可以使用 Vue-CLI 提供的工具查看 webpack 的配置文件(Vue-CLI 对 webpack 做了深度的封装,在项目中看不到)
1 | $ vue inspect > output.js #将获取到的webpack配置文件输出到output.js 文件中 |
单文件组件(*.vue)在运行时候是不需要编译器的,浏览器不支持这些单文件组件打包的时候会将这些组件转换成js对象,并将模板转换为render函数所以单文件组件在运行时是不需要编译器的
源码解析
入口开始
寻找入口文件
以dist/vue.js 的构建过程为例
执行构建
1
2
3npm run dev
# "dev": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --sourcemap --environment TARGET:web-full-dev"
# --environment TARGET:web-full-dev 设置环境变量 TARGETscripts/config.js 的执行过程
- 作用:生成 rollup 构建的配置文件
- 使用环境变量 TARGET = web-full-dev
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9// 判断环境变量是否有 TARGET,如果有的话使用genConfig()生成rollup配置文件
// 获取环境变量TARGET (package.json/scripts中设置)
if (process.env.TARGET) {
module.exports = genConfig(process.env.TARGET)
} else {
// 否则获取全部配置
exports.getBuild = genConfig
exports.getAllBuilds = () => Object.keys(builds).map(genConfig)
}genConfig(name)
- 根据环境变量 TARGET 获取配置信息
- builds[name] 获取生成配置的信息
1 | // Runtime+compiler development build (Browser) |
resolve()
- 获取入口和出口文件的绝对路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11const aliases = require('./alias')
// 将传入的路径转换为绝对路径
const resolve = p => {
// 根据路径中的前半部分去 alias 模块中找别名对应的路径
const base = p.split('/')[0] // web / dist
if (aliases[base]) {
return path.resolve(aliases[base], p.slice(base.length + 1))
} else {
return path.resolve(__dirname, '../', p)
}
}alias 模块
定义别名,简化路径书写
1 | // 将传入的参数 转化为 绝对路径 |
整个构建过程是把 src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 构建成 dist/vue.js,如果设置 --sourcemap 会生成 vue.js.map,入口文件即为entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
从入口文件开始分析vue的源码
vue源码模块比较多,我们带着问题来查看源码,方便我们阅读源码,下面通过查看入口文件来解决下面的问题
如果同时设置template和render此时会渲染什么?
1 | const vm = new Vue({ |
入口文件代码:src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
1 | // 保留vue实例的$mount方法(把生成的BOM挂载到页面上) |
通过源码可以知道
- el 不能是 body 或者 html 标签
- 如果没有 render,会把 templat e转换成 render 函数
- 如果有 render 方法直接调用 mount 挂载 DOM
这里有个问题:$mount在什么时候调用?
最简单的方式就是通过调试代码查看call Stack(调用堆栈)清晰看到方法调用过程
注意:如果你最后执行了
npm run build操作,dist/vue.js中的最后一行的sourceMap映射//# sourceMappingURL=vue.js.map会被清除,所以如果想在调试过程看到src源码,需要重新npm run dev开启代码地图。
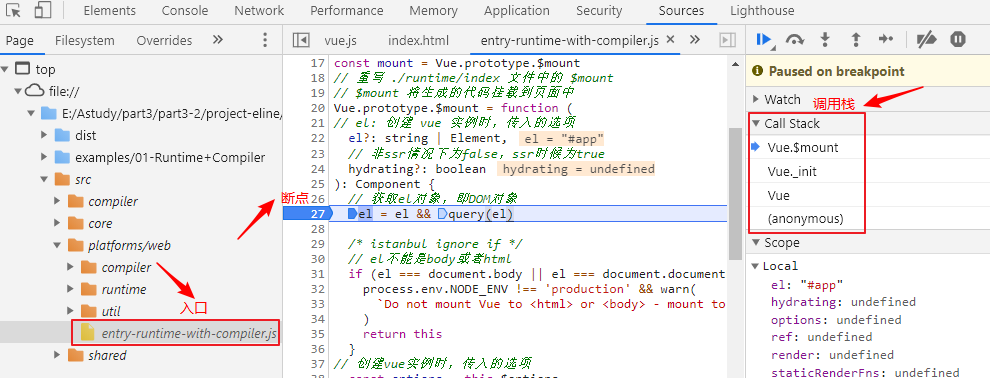
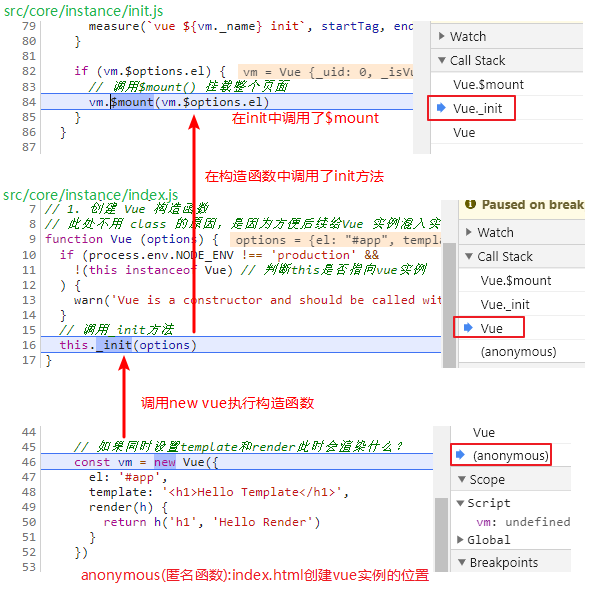
从而我们得知:$mount 是 _init() 调用的,同时也验证了开始的答案:如果 new Vue 同时设置了 template 和 render() ,此时只会执行 render()
Vue 的构造函数在哪? Vue 实例的成员 / Vue 的静态成员 从哪里来的?
Vue 的初始化
四个导出 Vue 的模块
src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js完整版- web 平台相关的入口,重点实现编译
- 重写了平台相关的
$mount()方法,将template转换成render函数 - 注册了
Vue.compile()方法,传递一个HTML字符串返回render函数
src/platforms/web/runtime/index.jsweb平台相关- 注册和平台相关的全局指令:
v-model、v-show - 注册和平台相关的全局组件:
v-transition、v-transition-group - 全局方法:
__patch__:把虚拟DOM转换成真实DOM$mount:挂载方法,将DOM渲染到页面中
src/core/index.js- 与平台无关
- 设置了
Vue的静态方法,initGlobalAPI(Vue)
src/core/instance/index.js- 与平台无关
- 定义了构造函数,调用了
this._init(options)方法 - 给
Vue中混入了常用的实例成员
初始化 Vue 的静态方法
可参考 Vue 全局 API 文档
在src/core/index.js中注册了vue的静态方法initGlobalAPI,在src/core/global-api/index.js中初始化vue的静态方法,源码如下:
1 | export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) { |
初始化 vue的实例成员
可参考 Vue 实例 文档
通过刚才调试 $mount 调用我们可以看到 vue 的构造函数和初始化 vue 的实例成员是在src/core/instance/index.js中定义,源码如下:
1 | // 1. 创建 Vue 构造函数 |
实例成员 - init
- initMixin(Vue)
- 注册 vm 的 _init() 方法,初始化 vm
- src/core/instance/init.js
1 | export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) { |
实例成员 - initState
- initState(vm)
- 初始化 vm 的 _props/methods/_data/computed/watch
- src/core/instance/state.js
1 | import { observe } from '../observer/index' |
首次渲染过程
- Vue 初始化完毕,开始真正的执行
- 调用 new Vue() 之前,已经初始化完毕
- 通过调试代码,记录首次渲染过程
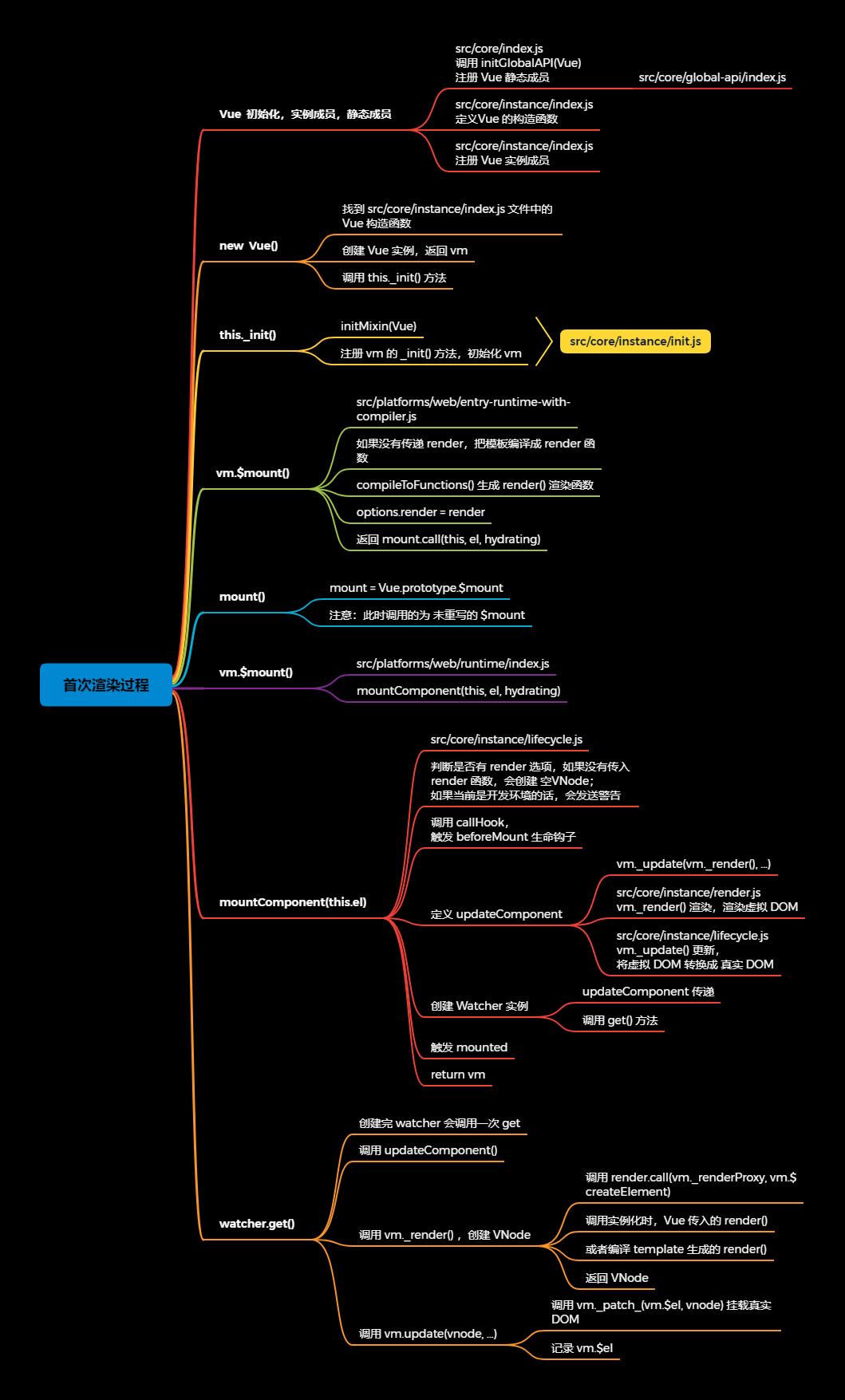
1.在 src/core/index.js 中调用 initGlobalAPI(Vue) ,初始化 Vue 静态成员
initGlobalAPI(Vue) 在 src/core/global-api/index.js 中定义
2.在 src/core/instance/index.js 中,定义 Vue 的构造函数
3.在 src/core/instance/index.js ,调用多个注册 Vue 实例成员的方法,实现 Vue 的初始化
4.执行 new Vue() 时,会找到 src/core/instance/index.js 文件中的 vue 构造函数,并创建 Vue 的实例,调用 init() 方法
5._init() 是在 src/core/instance/init.js 文件中定义的的 initMixin() 中注册的,初始化 vm,并且调用 vm.$mount() 挂载整个页面
6.首先,会找到 src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 中定义的 mount() 方法 ,根据用户传入的 this.options ,判断是否传入了 render 函数,若没有,则调用 compileToFunctions() 将 template 转化为 render 函数,并将 render 函数存入 options.render 中。最后会返回 mount.call(this, el, hydrating),调用 mount()
7.然后,会执行 src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js 中定义的 $mount(),并返回 mountComponent(this, el, hydrating),运行时版本不会执行这个入口
8.mountComponent() 在 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 中定义,
1)会先判断用户是否传入 render 函数,如果没有传入 render 函数,会创建空 VNode;并且如果当前是开发环境的话,会发送警告
2)会调用 callHook(),触发 beforeMount 生命钩子;
3)定义 updateComponent (更新组件),实现挂载,会调用 vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating) ,vm._update()在 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 中定义,将 VNode 转换为真实 DOM,vm._render 在 src/core/instance/render.js 中定义,渲染虚拟 DOM;
4)创建 Watcher 实例,并且传递 updateComponent ,调用 get() 方法
9.在 src/core/observer/watcher.js 中定义 Watcher 类,
1)创建完 watcher 会调用一次 get();
2)调用 updateComponent();
3)调用 vm._render() ,创建 VNode;
4)调用 vm.update(vnode, …)
10.在 mountComponent() 的最后,会触发 mounted 生命钩子,此时页面渲染完成;并返回 vm (Vue 实例)。
数据响应式原理
数据响应式和双向绑定机制是使用数据开发驱动的基石,数据响应式:数据发生改变时候自动更新视图,不需要手动更新DOM。
在数据响应式中我们可能会遇到下面这些问题,通过查看源码来回答这些问题:
- vm.msg = { count: 0 } 重新给属性赋值,是否是响应式的?
- vm.arr.push(4) 视图是否会更新?
- vm.arr[0] = 4 给数组元素赋值,视图是否会更新?
- vm.arr.length = 0 修改数组的 length,视图是否会更新?
响应式处理的入口
整个响应式处理的过程是比较复杂的,我们先找到入口,在循循渐进方式去查看内部的原理
在上面实例成员 - initState这节中我们可以在 initState() 中使用到了 observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */) ,当没有 data 属性时候的 vm._data 设置为空对象,赋值为 true 设置为响应式的,通过这个方法找到了入口文件,即在 src/core/observer/index.js 中创建 observe 方法,这个方法的作用是:负责为每一个 Object 类型的 value 创建一个 observer 实例
1 | /** |
Observer
- src/core/observer/index.js
- 对对象做响应化处理
- 对数组做响应化处理
1 | /** |
walk(obj)
遍历 obj 的所有属性,为每一个属性调用 defifineReactive() 方法,设置 getter/setter
对象响应式处理 defifineReactive
1 | defifineReactive(obj, key, val, customSetter, shallow)' |
- 为一个对象定义一个响应式的属性,每一个属性对应一个
dep对象 - 如果该属性的值是对象,继续调用
observe - 如果给属性赋新值,继续调用
observe - 如果数据更新发送通知
1 | /** |
数组的响应式处理
- Observer 的构造函数中
1 | // 获取 arrayMethods 特有的成员 返回的是包含名字的数组 |
处理数组修改数据的方法 arrayMethods
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49import { def } from '../util/index'
const arrayProto = Array.prototype
// 使用数组的原型创建一个新对象,对象原型指向了数组的prototype
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto)
// 修改数组元素的方法,这些方法都会修改数组的原数组
// 数组原生方法不知道dep存在,更不会调用dep.notify()
const methodsToPatch = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
'unshift',
'splice',
'sort',
'reverse'
]
/**
* Intercept mutating methods and emit events
*/
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) {
// cache original method
// 保存数组原方法
const original = arrayProto[method]
// 调用Object.defineProperty()重新定义修改数组的方法
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator (...args) {
// 执行数组的原始方法
const result = original.apply(this, args)
// 获取数组对象的ob对象
const ob = this.__ob__
let inserted
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args
break
case 'splice':
// splice第三个元素是新增的元素
inserted = args.slice(2)
break
}
// 对插入的新元素,重新遍历数组元素设置为响应式数据
if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted)
// notify change
// 调用修改了数组的方法,调用数组的ob对象发送通知
ob.dep.notify()
return result
})
})
dep 类
- 依赖对象
- 记录 watcher 对象
- depend() – watcher 记录对应的 dep
- 发布通知
src/core/observer/index.js1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33export function defineReactive (...) {
// 创建依赖对象实例 收集每一个属性的依赖
const dep = new Dep()
...
// 判断是否递归观察子对象,并将子对象属性都转换成 getter/setter,返回子观察对象
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
...
get: function reactiveGetter () {
...
// 如果存在当前依赖目标,即 watcher 对象,则建立依赖
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
// 如果子观察目标存在,建立子对象的依赖关系
if (childOb) {
// 为当前子对象收集依赖
childOb.dep.depend()
// 如果属性是数组,则特殊处理收集数组对象依赖
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
// 返回属性值
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
...
// 派发更新(发布更改通知)
dep.notify()
}
})
}
src/core/observer/dep.js1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86/* @flow */
import type Watcher from './watcher'
import { remove } from '../util/index'
import config from '../config'
let uid = 0
/**
* A dep is an observable that can have multiple
* directives subscribing to it.
*/
// dep 是个可观察对象,可以有多个指令订阅它
export default class Dep {
// 静态属性,watcher 对象
static target: ?Watcher;
// dep 实例 Id
id: number;
// dep 实例对应的 watcher 对象/订阅者数组
subs: Array<Watcher>;
constructor () {
this.id = uid++
this.subs = []
}
// 添加新的订阅者 watcher 对象
addSub (sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
// 移除订阅者
removeSub (sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub)
}
// 将观察对象和 watcher 建立依赖
depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
// 如果 target 存在,把 dep 对象添加到 watcher 的依赖中
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
// 数据更新时候会调用notify方法
// 发布通知
notify () {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
// 克隆subs数组
const subs = this.subs.slice()
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
// subs aren't sorted in scheduler if not running async
// we need to sort them now to make sure they fire in correct
// order
// 按照watcher的创建顺序进行排序
subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id)
}
// 调用每个订阅者的update方法实现更新
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update()
}
}
}
// The current target watcher being evaluated.
// This is globally unique because only one watcher
// can be evaluated at a time.
// Dep.target 用来存放目前正在使用的 watcher
// 全局唯一,并且一次也只能有一个 watcher 被使用
Dep.target = null // 存储当前正在执行的目标对象
const targetStack = []
/* 入栈并将当前 watcher 赋值给 Dep.target
父子组件嵌套的时候先把父组件对应的watcher入栈,
载入处理子组件的watcher,子组件处理完后,再把父组件对应的watcher出栈,继续操作
*/
export function pushTarget (target: ?Watcher) {
// 每一个组件都有一个watcher,组件中存在嵌套时,需要存储父组件中的 watcher
targetStack.push(target)
Dep.target = target
}
export function popTarget () {
// 当子组件渲染完之后,会把对应的watcher从栈中弹出,继续执行父组件渲染
targetStack.pop()
Dep.target = targetStack[targetStack.length - 1]
}
- 在
defineReactive()的getter中创建dep对象,并判断Dep.target是否有值,如果有, 调用dep.depend() dep.depend()内部调用Dep.target.addDep(this),也就是watcher的addDep()方法,它内部最先调用dep.addSub(this),把watcher对象,添加到dep.subs.push(watcher)中,也就是把订阅者添加到dep的subs数组中,当数据变化的时候调用watcher对象的update()方法- 什么时候设置的
Dep.target? 通过首次渲染的案例调试观察。调用mountComponent()方法的时候,创建了渲染watcher对象,执行watcher中的get()方法 get()方法内部调用pushTarget(this),把当前Dep.target = watcher,同时把当前watcher入栈, 因为有父子组件嵌套的时候先把父组件对的watcher入栈,再去处理子组件的watcher,子组件的处理完毕 后,再把父组件对应的watcher出栈,继续操作Dep.target用来存放目前正在使用的watcher。全局唯一,并且一次也只能有一个watcher被使用
Watcher 类
Watcher 分为三种,Computed Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
渲染 Watcher 的创建时机
src/core/instance/lifecycle.js
1 | export function mountComponent ( |
- 渲染
wacher创建的位置lifecycle.js的mountComponent函数中 Wacher的构造函数初始化,处理expOrFn(渲染 watcher 和侦听器处理不同)- 调用
this.get(),它里面调用pushTarget()然后this.getter.call(vm, vm)(对于渲染wacher调用updateComponent),如果是用户wacher会获取属性的值(触发get操作) - 当数据更新的时候,
dep中调用notify()方法,notify()中调用wacher的update()方法 update()中调用queueWatcher()queueWatcher()是一个核心方法,去除重复操作,调用flushSchedulerQueue()刷新队列并执行watcherflushSchedulerQueue()中对wacher排序,遍历所有wacher,如果有before,触发生命周期的钩子函数beforeUpdate,执行wacher.run(),它内部调用this.get(),然后调用this.cb()(渲染wacher的cb是noop)整个流程结束
响应式处理过程总结
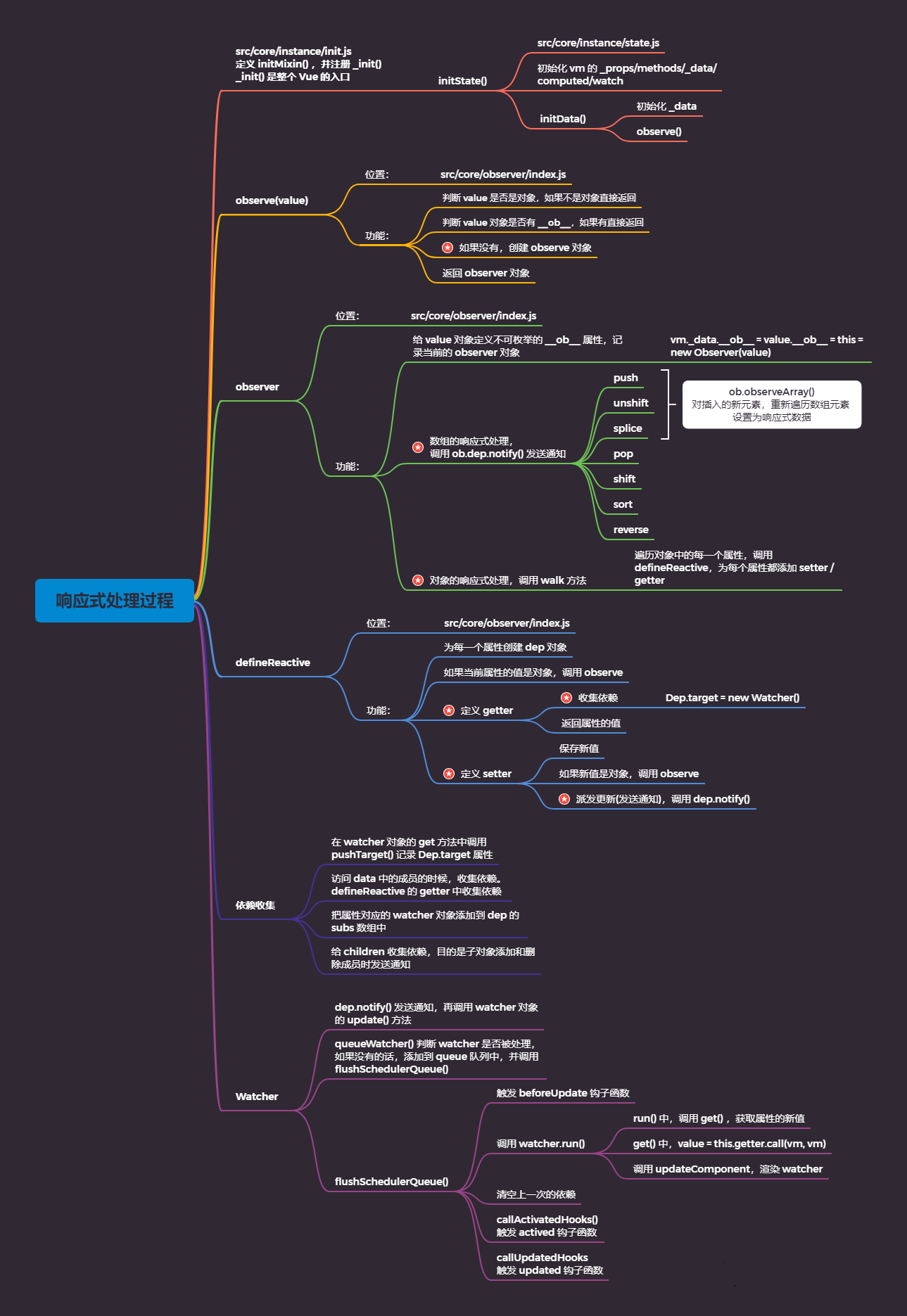
使用 new Vue() 创建 Vue 实例时,触发
src\core\instance\index.js中的 Vue 构造函数,从而调用_init()方法,_init()方法是在initMixin()中进行注册的;在src/core/instance/init.js中导出initMixin(),并在initMixin()中注册_init()方法,_init()是整个 Vue 的入口;在_init()中调用initState()初始化 vm 的_props/methods/_data/computed/watch,在initState方法中调用了initData(),initData()是把data中的成员 注入到 Vue 实例中,并且调用observe(data)将data对象转化成响应式的对象。在
src/core/observer/index.js中定义observe(),observe()是数据响应式的入口,判断
value是否是对象 或者value是否是VNode的实例,如果不是对象,但是是VNode则直接返回;判断
value对象是否有__ob__,- 如果有直接返回
observer对象,类似于缓存,提升性能 - 如果没有,则创建
observe对象,返回observer对象。
- 如果有直接返回
创建
observer对象,即new一个Observer的实例。Observer构造函数 在src/core/observer/index.js中定义,给当前传入的value对象(即vm._data) 添加不可枚举的__ob__属性,并将当前的observer实例对象挂载到value.__ob__中,然后再进行数组的响应式处理和对象的响应式处理。- 数组的响应式处理,就是重写数组中修改原数组的方法,如
push、pop、shift等,当执行数组的push、unshift、splice(插入或替换元素)方法 ,对数组中新插入的元素,会调用observer实例的observeArray()方法,重新遍历数组元素,并将其设置为响应式数据。最后,调用数组的observer对象中的dep依赖的notify()方法,进行发送通知操作。 - 对象的响应式处理,就是调用 observer 对象的
walk()方法,遍历对象中的每一个属性,调用defineReactive(),为每一个属性添加 setter / getter。
- 数组的响应式处理,就是重写数组中修改原数组的方法,如
defineReactive方法,为每一个属性创建dep实例对象,dep负责为当前属性key收集依赖,即收集当前观察属性的Watcher。如果当前属性的值是对象,会进行深度监听,并调用observe。defineReactive中利用Object.defineProperty()为属性添加getter和setter。其中,getter的作用是收集依赖,即为当前的Watcher对象添加依赖,1个watcher会对应多个dep(即,要观察的属性很多) 。如果这个属性的值是对象,那也要给子对象添加依赖,最后返回属性的值。在setter中,先保存新值,如果新值是对象,也要调用observe,观察子对象并返回子对象的observer对象,然后,调用dep.notify(),进行派发更新(发送通知)。收集依赖时,在
watcher对象的get方法中调用pushTarget,记录Dep.target属性。访问data中的成员的时候收集依赖,defineReactive的getter中收集依赖。把属性对应的watcher对象添加到dep的subs数组中,给childOb收集依赖,目的是子对象添加和删除成员时发送通知。在数据发生变化的时候,会调用
dep.notify()发送通知,在dep.notify()中会调用watcher对象的update()方法,update()中的调用的queueWatcher()去判断watcher是否被处理,如果watcher没有被处理,则添加到queue队列中,并调用flushScheduleQueue()。在
flushScheduleQueue()中,会渲染Watcher, 触发beforeUpdate生命钩子函数,并调用watcher.run(),run()中调用get(),获取属性的新值,get()中,使用value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)获取新值,调用this.cb(),即调用updateComponent,渲染watcher。最后,调用resetSchedulerState(),清空上一次的依赖;调用callActivatedHooks(activatedQueue),触发actived钩子函数;调用callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue),触发updated钩子函数。
之前提出的问题现在答案就很明确了
- vm.msg = { count: 0 } 重新给属性赋值,是否是响应式的?
是响应式的 - vm.arr.push(4) 视图是否会更新?
视图是会更新 - vm.arr[0] = 4 给数组元素赋值,视图是否会更新?
视图不会更新,数组赋值可以使用vm.arr.splice(0,1,4) - vm.arr.length = 0 修改数组的 length,视图是否会更新?
视图不会更新,清空数组可以使用vm.arr.splice(0)
处理数组响应式的时候并没有遍历数组中的所有属性,而是遍历所有元素把是对象的元素转换为响应式对象,并没有处理数组对象的属性,数组中元素会很多,处理的会导致性能问题
实例方法/数据
vm.$set
功能
向响应式对象中添加一个属性,并确保这个新属性同样是响应式的,且触发视图更新。它必须用于向响应式对象上添加新属性,因为 Vue 无法探测普通的新增属性 (比如 this.myObject.newProperty = 'hi')
1 | vm.$set(obj, 'foo', 'test') |
注意:对象不能是 Vue 实例,或者 Vue 实例的根数据对象($data)。
源码
定义位置
- vue.set()
src/core/global-api/index.js
1 | // 静态方法 set/delete/nextTick |
- vm.$set()
src/core/instance/index.js
1 | // 注册 vm 的 $data/$props/$set/$delete/$watch |
set() 方法
src/core/observer/index.js1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52/**
* Set a property on an object. Adds the new property and
* triggers change notification if the property doesn't
* already exist.
*/
// 设置对象的属性。添加新的属性,如果该属性不存在,则触发更改通知
export function set (target: Array<any> | Object, key: any, val: any): any {
// 判断target是否是undefined或者是原始值,因为不能为undefined和原始值增加属性
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
(isUndef(target) || isPrimitive(target))
) {
warn(`Cannot set reactive property on undefined, null, or primitive value: ${(target: any)}`)
}
/* 数组处理 */
// 判断 target 是否是数组,key是否是合法的索引
if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
// 判断当前key和数组length的最大值给length
// 当我们调用$set传递的索引有可能超过数组的length属性
target.length = Math.max(target.length, key)
// 通过 splice 对 key 位置的元素进行替换
// splice在array.js进行了响应化的处理
target.splice(key, 1, val)
return val
}
/* 对象处理 */
// 如果 key 在对象中已经存在且不是原型成员 直接赋值
if (key in target && !(key in Object.prototype)) {
target[key] = val
return val
}
// 获取 target 中的 observer 对象
// 响应式处理中会给每个对象增加一个__ob__属性,__ob__存储的是observer对象
const ob = (target: any).__ob__
// 如果 target 是 vue 实例或者 $data 直接返回($data的ob.vmCount值为1,其他对象为0 )
if (target._isVue || (ob && ob.vmCount)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'Avoid adding reactive properties to a Vue instance or its root $data ' +
'at runtime - declare it upfront in the data option.'
)
return val
}
// 如果 ob 不存在,target 不是响应式对象直接赋值
if (!ob) {
target[key] = val
return val
}
// 如果ob对象存在,调用 defineReactive 把 key 设置为响应式属性
defineReactive(ob.value, key, val)
// 发送通知 (这里可以这样调用原因是,在收集依赖的时候为每一个子对象创建了childob,并给childob的ob也收集了依赖,所以这里可以直接发送通知)
ob.dep.notify()
return val
}
vm.$delete
功能
删除对象的属性。如果对象是响应式的,确保删除能触发更新视图。这个方法主要用于避开 Vue不能检测到属性被删除的限制,但是你应该很少会使用它。
1 | vm.$delete(vm.obj, 'msg') 1 |
注意:目标对象不能是一个 Vue 实例或 Vue 实例的根数据对象。
源码
定义位置
- Vue.delete()
1 | // 静态方法 set/delete/nextTick |
- vm.$delete()
1 | // 注册 vm 的 $data/$props/$set/$delete/$watch |
del()方法
1 | /** |
vm.$watch
观察 Vue 实例变化的一个表达式或计算属性函数。回调函数得到的参数为新值和旧值。表达式只接受监督的键路径。对于更复杂的表达式,用一个函数取代。
1 | vm.$watch( expOrFn, callback, [options] ) |
- expOrFn:要监视的 $data 中的属性,可以是表达式或函数
- callback:数据变化后执行的函数
- 函数:回调函数
- 对象:具有 handler 属性(字符串或者函数),如果该属性为字符串则 methods 中相应的定义
- options:可选的选项
- deep:布尔类型,深度监听
- immediate:布尔类型,是否立即执行一次回调函数
1 | const vm = new Vue({ |
三种类型的 Watcher 对象
- 没有静态方法,因为
$watch方法中要使用Vue的实例 - Watcher 分三种:计算属性 Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
- 创建顺序:计算属性 Watcher(
id:1)、用户 Watcher (侦听器)(id:2)、渲染 Watcher(id:3) - 执行顺序:按照id从小到大顺序,与创建顺序相同
- vm.$watch()
src/core/instance/state.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 //$watch 监视数据变化
Vue.prototype.$watch = function (
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: any,
options?: Object
): Function {
// 获取 vue 实例 this
const vm: Component = this
if (isPlainObject(cb)) {
// 判断如果 cb 是对象执行 createWatcher
return createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
}
options = options || {}
// 标记为用户 watcher
options.user = true
// 创建用户 watcher 对象
const watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
// 判断 immediate 如果为 true
if (options.immediate) {
// 立即执行一次 cb 回调,并且把当前值传入
//try...catch作用: 不确定回电函数是否安全,确保回电函数执行错误不会影响代码执行
try {
cb.call(vm, watcher.value)
} catch (error) {
handleError(error, vm, `callback for immediate watcher "${watcher.expression}"`)
}
}
// 返回取消监听的方法
return function unwatchFn () {
watcher.teardown()
}
}
异步更新队列 -nextTick()
Vue 更新 DOM 是异步执行的,批量的
在下次 DOM 更新循环结束之后执行延迟回调。在修改数据之后立即使用这个方法,获取更新后的 DOM。
1 | vm.$nextTick(function () { /* 操作 DOM */ }) / Vue.nextTick(function () {}) |
定义位置
src/core/instance/render.js
1 | Vue.prototype.$nextTick = function (fn: Function) { |
源码
- 手动调用
vm.$nextTick() - 在
Watcher的queueWatcher中执行nextTick() - src/core/util/next-tick.js
1 | /* @flow */ |